Acute Prostatitis – infectious-inflammatory lesion of the prostate gland, accompanied by swelling and the formation of purulent lesions in tissues of the prostate. Symptoms of acute Prostatitis are dependent on the stage (catarrhal, follicular, parenchymatous, abscessed) and dizuriceskie disorders, pain in the perineum, fever, intoxication can. The diagnosis is based on data palpation of the prostate, ultrasound and Doppler studies of the prostate gland, examination of discharge urethra, and secretions of the prostate gland. The treatment of acute Prostatitis includes the use of anti-microbial therapy, NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, analgesics, immune modulators, physiotherapy.
Acute and chronic Prostatitis is the most common and socially significant diseases of the male. In clinical urology, Prostatitis, of men diagnosed with 30-58% in the reproductive and working age (30-50 years). For acute Prostatitis, of sexual function and fertility, disorders of Psycho accompanied by disturbances-emotional Status and the social dis-adapt to the pulsation.
Causes of acute Prostatitis
Causative agent of acute Prostatitis occur predominantly non-specific infectious agents that penetrate into the tissue of the prostate Gram-negative (Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Proteus) or Gram-positive (staphylococci, enterococci, streptococci)
Often acute Prostatitis may infections by pathogens of the urogenital:
- Chlamydia,
- Trichomoniasis,
- ureaplazmoza,
- Gonorrhea,
- mycoplasmosis,
- Candidiasis and others.
Most often, penetration of antimicrobial agent in prostatic tissue TRANS-canalicular occurs through the channels of the gland, which is located in the wall of the posterior urethra. Therefore, Urethritis, each Genesis is very often complicated by acute Prostatitis. Rare microbial Flora is located in the prostate of the urinary bladder acute cystitis. The Integration of the pathogen in the prostate at elevated considerably facilitates intra-urethral pressure (reprehenderat, stones in the urethra), the implementation of the endourethral Manipulation (bougienage urethra, urinary bladder catheterization, ureteroscopy, cystoscopy, etc.).
In addition, acute Prostatitis can be a consequence of hematogenous infection, because the conditions of the blood supply to the prostate anastomoses with a well-developed System of arterial and venous. In the case of hematogenous Drift germs can get into the prostate tissue from remote pus foci in case of tonsillitis, Sinusitis, caries, cholecystitis, Bronchitis, pyoderma and others. Perhaps lymphogenous infection of the prostate from the bowel with anal fissures, proctitis, colitis.
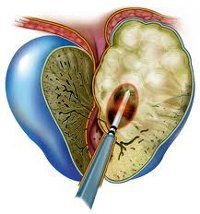
To non-transferable factors, which belong to the development of acute Prostatitis, Stagnation in the veins of the pelvis and the violation of the Drainage acini of the prostate. Stagnation can live by disritmia sex and sexual disorders – practice interrupted intercourse, the lack or the irregularity of a sexual life, excessive sexual activity, etc., Pathological deposition of blood in the venous circulation of the small pelvis can be celebrated in a lack of exercise, frequent constipation, colds, chronic (especially alcohol) intoxication, varicose veins of the pelvis.
Form of acute Prostatitis
In the development of acute Prostatitis the following forms, at the same time its phases are:
- catarrhal,
- follicular,
- Parenchyma,
- abscessed.
Acute Prostatitis begins with catarrhal inflammatory changes of the mucous membrane and submucosa excretory ducts of the various lobules of the gland. In the future, the swelling of the walls of the bile ducts, Stagnation, promotes Muco-purulent secretion in the follicles of the prostate gland and the inflammation of the lobules in connection with the develop – localized suppuration-acute follicular Prostatitis. When multiple lesions of the lobules, and diffuse involvement of parenchymatous and interstitial tissues of the prostate-purulent inflammation, acute Prostatitis is entering its next Phase – parenchyma. In the case of a merger of small ulcers in the large fire pit abscess of the prostate, and open into the urethra, perineum, rectum, or bladder is formed.
Symptoms of acute Prostatitis
The clinical symptoms in acute Prostatitis correspond to the stages of the process. The General symptoms are pain, urination disorders and poisoning.
In the acute catarrhal stage of Prostatitis feeling and pain heavy in the dam. Dizuriceskie disorder is characterized by painful urination, especially at night. The body temperature remains in the normal range, a slightly elevated; intoxication missing. On Palpation, the examination of the prostate not changed or slightly increased, little painful. The research of the secret of the prostate detects an increase in the cells, the accumulation of Muco-purulent threads. In the urine during the emptying of the excretory ducts of the acini leukocytes appear. The Massage of the prostate, in General, not possible because of the pain. The treatment started at the stage of acute catarrhal Prostatitis, leads to recovery after 7-10 days.
The follicular Form of acute Prostatitis occurs heller, accompanied by dull pain in the Perineum, irradiating in the Penis, Anus, or the sacrum. Against this background, urination painful and difficult, until the development of acute urinary retention. The act of defecation in the case of acute follicular Prostatitis is also difficult because of the severe pain. Due to the increase in body temperature up to 38°C disturbed General well-being. Palpation per rectum increased determined, dense, intense, asymmetric prostate gland, sharply painful in the individual sections if digital examination. The urine collected after the scanning of the prostate, large quantities of leukocytes and pus Thread that contains the muddy Sediment. The Massage for the purpose of obtaining the secret of the prostate gland in the Follicular Phase of acute Prostatitis is contraindicated. In the energetic treatment of acute follicular Prostatitis can be advantageously solved; otherwise, he goes into the next one, parenchymal Phase.
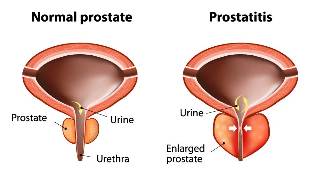
The clinic of acute parenchymatous Prostatitis develops rapidly. Characteristic of marked hyperthermia (up to 39-39,5°C and higher), chills, General weakness, Depression, appetite, thirst. First of all, the water is strong and learns more difficult, then can be terminated. Try emptying of the bladder or of the intestine accompanied by intense pain. Painful tenesmus, constipation, flatulence develop. The pain extends to the rectum, is throbbing in nature, forcing the patient to take the compelled position – supine position, with tipped legs. In the development of reactive inflammation of the rectum out of the Anus mucus.
Diffusely enlarged palpable determined, with blurred contours iron, extremely painful at the slightest touch. The Massage of the prostate in the parenchymal Phase of acute Prostatitis is contraindicated, categorically. Sometimes, due to a strong swelling of the para-rectal dietary fiber pain, and rectal examination can not. In the urine dramatically album expressed sanguinem cellam, pyuria. The result of the acute parenchymatous Prostatitis resolution of the disease may serve to the formation of an abscess of the prostate and chronic Prostatitis.
Diagnosis of acute Prostatitis
Detection and determination of the Phase of acute Prostatitis, the urologist carried out and is based on a complex physical, laboratory and instrumental investigation. Examination of the prostate via the rectum, it may. on the size, consistency, uniformity, and symmetry of the prostate; pain reactions, Foci, and signs of a purulent tissue Palpation of the prostate acute Prostatitis is very careful, without the art of persuasion and massaging movements. In the resulting secret of the prostate, an increase in the number of cells and Amyloid Taurus, the granules reduce the amount of lecithin.
In acute Prostatitis there is an increased leukocyturia in the third section of urine and the urine, the prostate is collected after the Palpation. For the isolation of the pathogen of acute Prostatitis, there is a culture of urine and vaginal discharge of the urethra with antibiotics, PCR should cockroaches-studies, sowing blood sanguinem cultura. The nature and severity of dizuricheskih disorders in acute Prostatitis, evaluated with the help of the uroflowmetries.

Uzi the prostate moderate pain syndrome performed transrectal; in the case of pronounced painful reactions – transabdominal. Anoscopically the Form of a rating, the size of the prostate, the presence of focal or diffuse changes, the stage of acute Prostatitis. The use of Doppler studies allows a detailed and differentiated to evaluate the vascularization of the prostate.
In the planning of surgical tactics in relation to the destructive forms of acute Prostatitis, the implementation of CT or MRI of the small pelvis is expedient.
The treatment of acute Prostatitis
The leading role in the treatment of acute Prostatitis belongs to the causal therapy. You will need to earliest possible date, anti-microbial (anti-bacterial, anti-viral, anti-trichomonal, antimycotic) drugs to suppress the propagation of microorganisms in iron and tissue of the urethra. With the aim of reducing muscle cramps and pain when urinating analgesics, antispasmodics, rectal candles with Anaesthesinum or Belladonna, thermal microclysters. In the complex therapy of acute Prostatitis, NSAIDs, enzymes, immune modulators, vitamins, infusions solutions.
Physiotherapy in acute Prostatitis occurs after resolution of acute symptoms. With the aim of, anti-inflammatory, decongestant, and analgesic actions, improving microcirculation, local immunity rectal electrophoresis, UHF-therapy, microwave therapy, prostate-apply Massage. In acute Prostatitis, the compliance with the bed rest, a diet shows, the sexual rest.
To prevent urinary retention, against the background of acute Prostatitis, the implementation of the catheterization of the urinary bladder, rather trocar cistostomii. In the case of abscess of the prostate, the need for surgical services - opening and Drainage of the abscess cavity.
The healing of acute Prostatitis are gland after the restoration of the structure of substances and their functions, the normalization of the juice of the prostate, the elimination of pathogens, which is used to inflammation, from biological fluids.
Prognosis and prevention
In General, timely and adequate causal treatment leads to a cupping of signs of acute Prostatitis. Abscess prostate cancer or chronic inflammation occurs in advanced cases.
Prevention of acute Prostatitis should be the rehabilitation of foci of infection in the body, the implementation of endovesical and endourethral manipulations in accordance with the rules of Asepsis, timely treatment of sexually transmitted diseases and Urethritis, the normalization of sexual life, and physical activity
























